
What is the Best Mobility Aid?
Have you looked at a lot of mobility aids and still don’t know which one is the best? Is it a bit difficult to choose? It doesn’t matter, this article can solve it.
From simple canes to more complex walkers, this guide is designed to provide clear, concise information to help you make your choice.

1. Canes (Walking Sticks)

Canes, also known as walking sticks, are the most basic type of mobility aid. They are primarily used for slight balance assistance and are suitable for individuals with minimal mobility challenges. Canes come in various styles, including adjustable, foldable, and quad-tip designs for enhanced stability.
Pros:
- Lightweight and Portable: Easy to carry and use on the go.
- Increases Independence: Enables users to move more freely and safely.
- Versatile Design Options: Available in various materials and styles to suit personal preferences.
Cons:
- Limited Support: Only suitable for those who need minimal assistance.
- Balance Dependent: Not ideal for users with significant balance issues.
2. Walkers

Standard walkers are basic frame-based mobility aids without wheels. They are designed to provide substantial support for those who need more than a cane but are still able to walk. Users lift the walker and place it forward with each step, making them most suitable for indoor use or smooth surfaces.
Pros:
- Stability and Support: Offer excellent support, reducing the risk of falls.
- Simple and Durable: Without complex parts, they are durable and require minimal maintenance.
- Cost-Effective: Generally more affordable than rollators or mobility scooters.
Cons:
- Requires Physical Effort: Each step requires lifting the walker, which can be strenuous over time or distance.
- Limited Mobility: Not as smooth or easy to maneuver as rollators, especially over uneven terrain.
3. Rollators

Rollators are an advanced type of walker equipped with wheels, brakes, and often a seat and storage. Designed for individuals who can walk but need significant support, rollators eliminate the need to lift the device, allowing for smoother movement.
Pros
- Enhanced Mobility: Wheels allow for easier and more fluid movement compared to standard walkers.
- Built-in Seating and Storage: Provides convenience for resting and carrying personal items.
- Adjustable and Versatile: Many models offer height adjustment and are suitable for both indoor and outdoor use.
Cons
- Heavier Than Standard Walkers: The added features make rollators bulkier and heavier.
- Cost: Generally more expensive than basic walkers due to additional features.
4. Wheelchairs

Wheelchairs are designed for individuals who cannot walk or have limited walking capabilities. They range from manual models, which require either user or caregiver propulsion, to electric wheelchairs that offer powered mobility. Wheelchairs are essential for users requiring significant mobility support.
Pros:
- Full Mobility Support: Ideal for individuals who cannot walk or have limited walking ability.
- Customizable: Many models can be tailored to specific needs, including seat size, leg rests, and control options for electric wheelchairs.
- Indoor and Outdoor Use: Especially electric wheelchairs, which are versatile for various environments.
Cons:
- Physical Effort for Manual Models: Requires upper body strength or a caregiver for propulsion.
- Charging and Maintenance for Electric Models: Requires regular charging and more maintenance.
5. Mobility Scooters

Mobility scooters are battery-powered devices ideal for people who can walk short distances but need assistance for longer ones. They typically feature a seat over two rear wheels, handlebars for steering, and a flat area for the feet. Mobility scooters are well-suited for outdoor use and can cover more distance than many other mobility aids.
Pros:
- Increased Range: Suitable for longer distances, enhancing independence outside the home.
- Comfort and Ease of Use: Offer a comfortable seated position and are easy to operate.
- Variety of Models: Available in different sizes and styles to suit various needs and preferences.
Cons:
- Higher Cost: Generally more expensive than simpler mobility aids.
- Storage and Transportation: Require adequate space for storage and may need special arrangements for transport.
6. Crutches

Crutches are a temporary mobility aid, often used during recovery from leg, foot, or ankle injuries. They come in two main types: underarm (axillary) crutches and forearm (elbow) crutches, each designed to redistribute weight from the legs to the upper body.
Pros:
- Temporary Mobility Support: Ideal for short-term use during injury recovery.
- Cost-Effective: Generally inexpensive compared to more complex mobility aids.
- Promote Fitness: Encourage upper body usage and strength.
Cons:
- Requires Upper Body Strength: Can be challenging to use for those with limited arm strength.
- Risk of Underarm Injury: Underarm crutches can cause discomfort or nerve damage if not used correctly.
7. Knee Scooters

Knee scooters, also known as knee walkers, are a mobility aid designed for foot, ankle, or lower leg injuries. They feature a platform for resting the injured leg while the user propels themselves with the healthy leg. These scooters often include handlebars for steering and brakes for safety.
Pros:
- Stability and Comfort: Provide a stable platform, reducing the risk of falling and offering more comfort than crutches.
- Ease of Mobility: Allow users to move faster and with less effort than crutches.
- Hands-Free Convenience: When not in motion, users can free their hands, unlike with crutches.
Cons:
- Not Suitable for Stairs: They cannot be used on stairs, limiting their use in certain environments.
- Size and Portability: Bulkier than crutches, requiring more space for storage and transport.
QuickView
| Mobility Aid | Main Features | Pros | Cons | Cost | Suitable for |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Canes | Basic support for balance | Lightweight,Cheap | Limited support, Balance dependent. | $15-$40 | Minimal support needs |
| Walkers | Frame-based, no wheels | Stable,Simple. | Physical effort required, Limited mobility. | $35-$60 | Moderate support needs |
| Rollators | Walkers with wheels, brakes, and often a seat | Enhanced mobility, Versatile. | Heavier than standard walkers. | $65-$200 | Greater support needs |
| Wheelchairs | Full-body support | Full support. | Manual requires strength, Electric needs charging. | $100-$500 | Limited or no walking ability |
| Mobility Scooters | Battery-powered | No need to push,Increased range. | Higher cost, Storage and transportation needs. | $400-$2000 | Needs assistance for longer distances |
| Crutches | Temporary support | Temporary support, Cheap. | Requires upper body strength,Risk of underarm injury. | $20-$50 | Temporary injuries |
| Knee Scooters | Rolling "Crutches" | Ease of mobility, Hands-free. | Not suitable for stairs, Larger size. | $100-$300 | Lower leg injuries |
Conclusion
Through the above content and table you should already know what the best Mobility Aid is. There is no answer because it depends on each person's situation. Of course, if you still don’t know what to choose, the Rollator is worth considering because it has the best value for money.
Recommend Products
-
 Sale
Sale
Standard - 300LBS Capacity Shower Stool
Original price $51.99From Original price $28.99Original price $51.99Current price $28.99From $28.99Current price $28.99OasisSpace Medical Square Shower Stool for Bathtub OasisSpace Square Shower Stool for Bathtub is approved as the highest standard(FDA) for medical...
View full detailsSaleOriginal price $51.99From Original price $28.99Original price $51.99Current price $28.99From $28.99Current price $28.99 -
 Sale
Sale
300LBS Capacity Raised Toilet Seat with Arms
Original price $120.99From Original price $69.99Original price $120.99Current price $69.99From $69.99Current price $69.99OasisSpace Raised Toilet Seat with Arms - Safe and Convenient OasisSpace Raised Toilet Seat with Arms provides stable support for users to sit dow...
View full detailsSaleOriginal price $120.99From Original price $69.99Original price $120.99Current price $69.99From $69.99Current price $69.99 -

350LBS Capacity 2 Wheel Walker
From Original price $39.99Original price$39.99From $39.99Current price $39.99Product Advantages OasisSpace's 350LBS Capacity walker offers a fusion of lightweight design and sturdy support, crafted from high-grade anodized ...
View full detailsFrom Original price $39.99Original price$39.99From $39.99Current price $39.99 -

Wall Mounted - 400LBS Capacity Teak Folding Shower Seat
From Original price $131.99Original price$131.99From $131.99Current price $131.99Advantages OasisSpace Teak Wall-Mounted Shower Seat adopts a folding design, which can save space to the greatest extent and can be folded up at a...
View full detailsFrom Original price $131.99Original price$131.99From $131.99Current price $131.99 -
 Sale
Sale
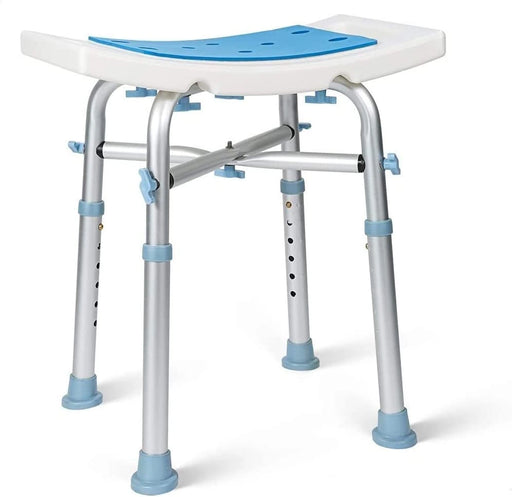
Padded & Bariatric - 500LBS Capacity Heavy Duty Shower Stool
Original price $57.99From Original price $36.99Original price $57.99Current price $36.99From $36.99Current price $36.99OasisSpace Medical Heavy Duty Bariatric Shower Stool OasisSpace Medical Heavy Duty Bariatric Shower Stool is approved by the FDA, which is the hig...
View full detailsSaleOriginal price $57.99From Original price $36.99Original price $57.99Current price $36.99From $36.99Current price $36.99 -
 Sale
Sale
300LBS Capacity Stand Alone Toilet Safety Rail
Original price $69.99From Original price $55.99Original price $69.99Current price $55.99From $55.99Current price $55.99OasisSpace Toilet Safety Rails - Fit Any Toilet OaisSpace stand-alone toilet safety rails provide sturdy support for the elderly and people with ...
View full detailsSaleOriginal price $69.99From Original price $55.99Original price $69.99Current price $55.99From $55.99Current price $55.99







